CERN addresses fundamental questions of the Universe at a facility of unprecedented scale. It is the world’s largest particle physics laboratory, making available complex, purpose-built particle accelerators and detectors, as well as computing technology, for its global research community (more than 13,000 researchers, from 75+ countries and 100+ nationalities) that spans various fields (particle-, nuclear-, astro- and accelerator physics, computing, engineering and beyond). As an international organisation, it brings together the community to develop and build state-of-the-art instruments and experiments, continually pushing the boundaries of facilities technology and engineering, computation and analytics.
The UK is one of CERN’s founding members and has been centrally involved throughout its history. Through a subscription –managed by the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC), on behalf of the UK – it currently contributes £144m per year to the CERN budget (16% of Member State subscriptions, 2019). This covers the building, operation and maintenance of the infrastructure, plus the governance and administration of CERN. The construction, maintenance, upgrade and operation of the experimental programme and the computing infrastructure is then additionally supported through funding from agencies of participating countries (for the UK, mainly by STFC). Over the past decade, the UK’s total investment in CERN through subscriptions and funding has averaged £152m per year.
STFC commissioned Technopolis to undertake an evaluation that would capture, demonstrate and measure the range of scientific, economic and social impacts emerging from the UK’s investment in and co-development of CERN, both from direct UK involvement and use, as well as wider influences of CERN on the UK. The study drew on multiple sources of evidence, including desk research, surveys, interviews, case studies and bibliometrics, to explore the various impacts of CERN on the UK.
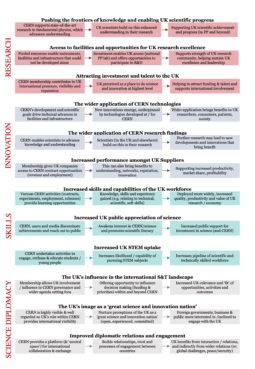
CERN’s strands of activity and engagement are multi-faceted, with a wide range of types of benefits and impact, flowing through a series of interrelated pathways. The study therefore defined and demonstrated 12 main areas of impact that flow to the UK, which are organised under the broad impact areas of research, innovation, skills and science diplomacy. The figure below summarises each of these impact pathways, which are then described in more detail in the report.
The highlights of the research are available here.
Full report of the study.




